Psoriasis is one of the most common chronic dermatoses. With such a pathological process, damage to the skin and skin appendages are noted. The high urgency of this problem lies in the fact that it leads to a deterioration in the quality of life of a sick person due to aesthetic ailments.
Most often, the first episode of psoriasis occurs in the age group of fifteen to forty-five. According to statistics, this disease is diagnosed in about three percent of the entire population. Moreover, the number of women and men with this pathology is in equal proportions.
There are several theories on the mechanism of development of psoriasis. The main one is the autoimmune theory, which states that this pathological process is formed as a result of an incorrect immune response to any external factor. An excessive immune response leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction in the skin layers, which triggers the mechanisms of division and multiplication of cellular structures. Furthermore, it is assumed that hereditary predisposition and exposure to various infectious agents may play a role in the development of this disease.
It is noted that psoriasis most often occurs in those people who:
- Having other dermatological conditions
- Having thin, dry skin
- Smoking and drinking alcohol
- Systematically coming into contact with irritating chemicals;
- They often injure the skin due to mechanical influences;
- Observe excessive hygiene;
- They are subject to severe stress;
- Having a reduced level of immune defense or using drugs that suppress immunity.
Depending on the symptoms of psoriasis, it is customary to classify this pathology into several forms:
- Plaque shape. This form is the classic version. It occurs in more than eighty percent of people. The clinical picture in this case is characterized by typical scaly plaques, which tend to grow peripherally;
- Teardrop shape. The disease proceeding in this form is accompanied by the appearance of numerous small foci on the surface of the skin. Such lesions can have a very different color, are raised above the surface of the skin and intensively peel off. As a rule, they do not increase in size, only their number increases;
- Exudative form. It is one of the most unfavorable options. In this case, bubbles and blisters filled with serous fluid form on the surface of the plaques. Most often, such elements undergo a secondary infection with the subsequent appearance of pus in them;
- Psoriatic onychodystrophy. It is characterized by the involvement of the nail plates in the pathological process, which become streaked and thickened. In most cases, the nails discolor, flake and break. In advanced cases, complete loss of the nail plate is possible;
- Psoriatic arthropathy. Symptoms of psoriasis in this case are manifested by inflammation of the joints and connective tissue. In some cases, this form develops on its own, but most often it is accompanied by skin manifestations;
- Psoriatic erythroderma. This form is characterized by a very severe course and is often fatal. The development of inflammation in large areas of the body is noted, which is accompanied by intense peeling and peeling of the skin.
The main symptoms of psoriasis
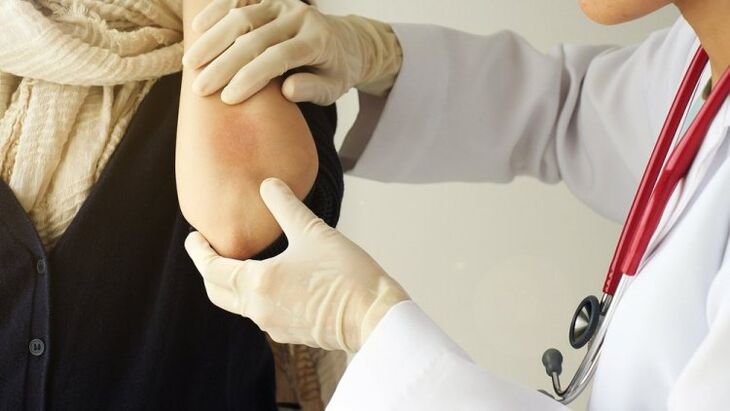
We will talk in more detail about the classic form. What does psoriasis look like? First, individual papules appear on the surface of the skin that have a pink or red color. These papules are covered in silvery-white scales that can be easily scraped off. Over time, the number of papules increases more and more, they begin to merge into plaques.
The plaques formed during this disease have a hyperemic and edematous appearance. In some cases, mild itchy skin may be present. Pathological foci tend to a rather rapid peripheral growth, and their surface is intensely scaly. Over time, the growth of the plates stops and their boundaries become clear. A specific sign of such a pathological process is a pseudoatrophic border, located along the periphery of the foci. In the stationary phase, a stagnant cyanotic tint appears on the surface of the plates.
Symptoms of regressing psoriasis are characterized by the gradual disappearance of desquamation, starting from the central part. Subsequently, the skin acquires a normal color, after which the tissue infiltration disappears.
Diagnosis and treatment of this disease
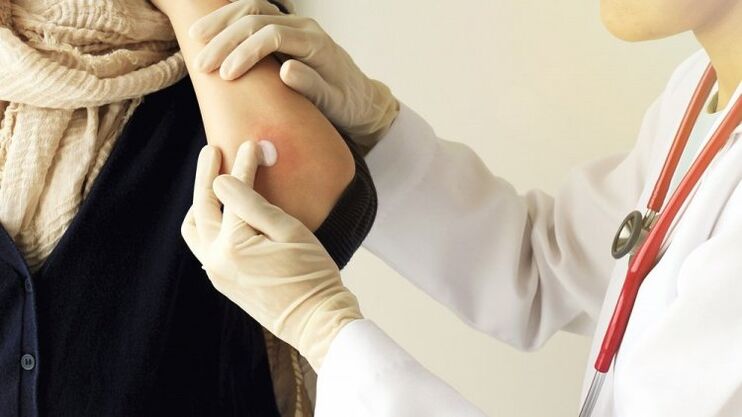
First, psoriasis is established on the basis of its clinical picture. There is a triad of specific phenomena that indicate this pathological process: stearin stain, terminal film and blood dew. The phenomenon of a stearic spot is that when the lesion is scraped, the peeling becomes more intense. If we continue to scrape, we notice a thin film peeling off and the appearance of a wet, hyperemic surface - the phenomenon of a terminal film. The phenomenon of blood dew implies the presence of punctate bleeding with further curettage.
Of the drugs for this disease, the following can be used:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- Cytostatics;
- Antihistamines;
- Keratolytic and anti-inflammatory ointments.
In addition, various physiotherapy treatments are widely used.
Prevention of exacerbations in psoriasis
To prevent flare-ups, it is recommended to avoid stressful situations, give up bad habits and eat right. In addition, you should limit any irritating effects on the skin and avoid contact with substances to which you are allergic.
























